
Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, isk-related subfamily. This member is a type I membrane protein, and a beta subunit that assembles with a potassium channel alpha-subunit to modulate the gating kinetics and enhance stability of the multimeric complex. This gene is prominently expressed in the kidney. A missense mutation in this gene is associated with hypokalemic periodic paralysis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- Ion transport
- Potassium ion transport
- Regulation of ion transmembrane transport
- Regulation of potassium ion transport
- Regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization
- Brugada syndrome 6
- Brugada syndrome
- Periodic paralysis
- Hypokalemic periodic paralysis, type 1
- Encephalopathy, neonatal severe, with lactic acidosis and brain abnormalities
- Brugada syndrome 6
- Brugada syndrome
- Periodic paralysis
- Hypokalemic periodic paralysis, type 1
- Encephalopathy, neonatal severe, with lactic acidosis and brain abnormalities
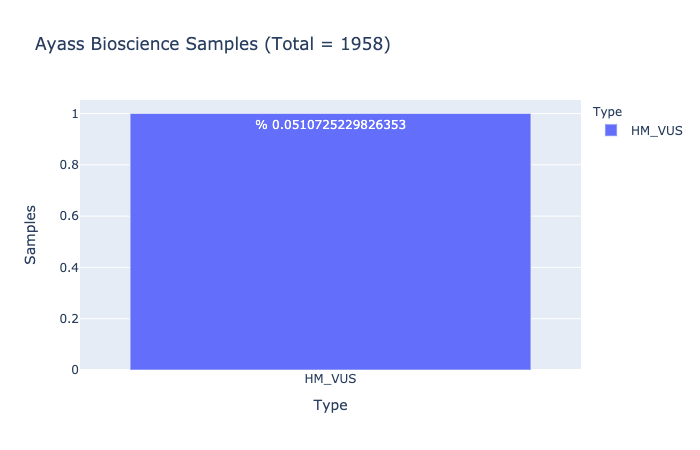
Based on Ayass Bioscience, LLC Data Analysis
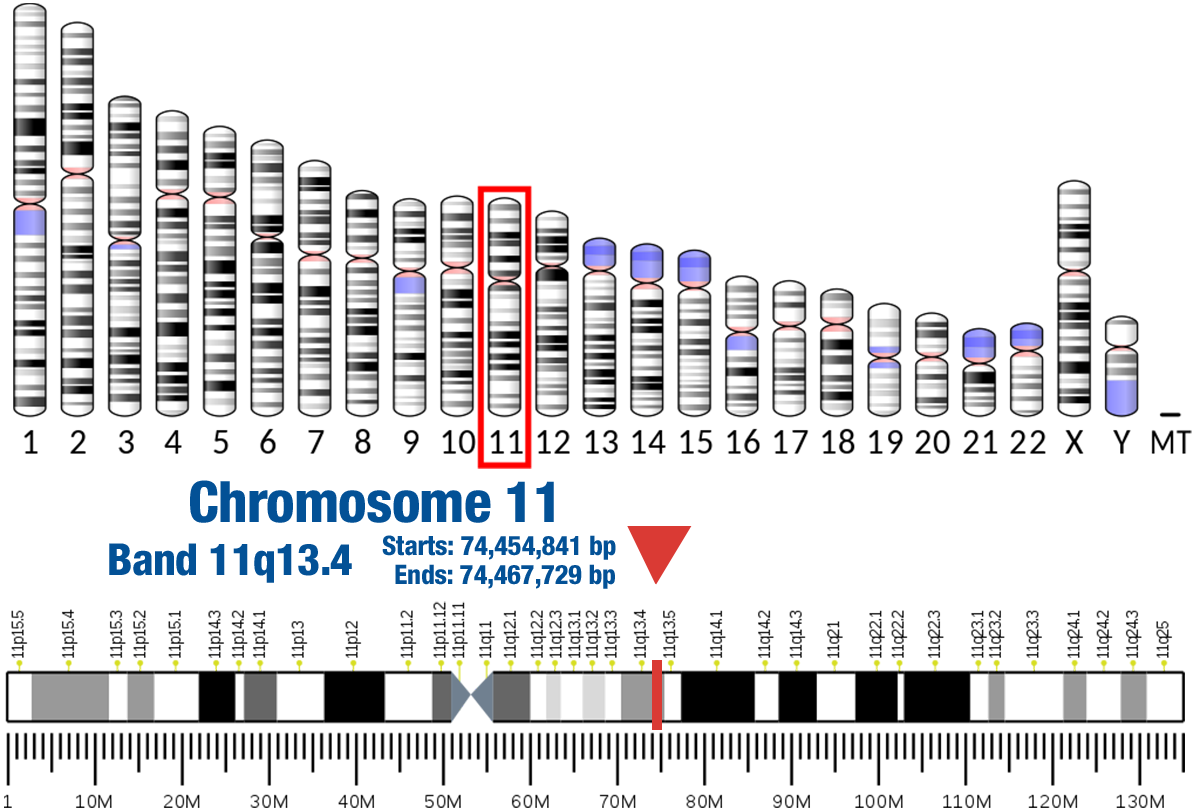
KCNE3 Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
Gene Location
HM-VUS Prevalence
% 0.0510725229826353
Ratio of samples with at least 1 High/Med VUS variant (Computed from Ayass Bioscience Samples)
High/Med VUS Variants
C=0.000139(35/251370,GnomAD_exome)
C=0.000127(16/125568,TOPMED)
C=0.000074(9/121138,ExAC)
C=0.00025(20/78698,PAGE_STUDY)
C=0.00006(2/31376,GnomAD)
C=0.0000(0/8766,ALFAProject)
C=0.0006(3/5008,1000G)
C=0.0031(9/2922,KOREAN)
C=0.0027(5/1832,Korea1K)
T=0.5(1/2,SGDP_PRJ)
C=0.5(1/2,SGDP_PRJ)

