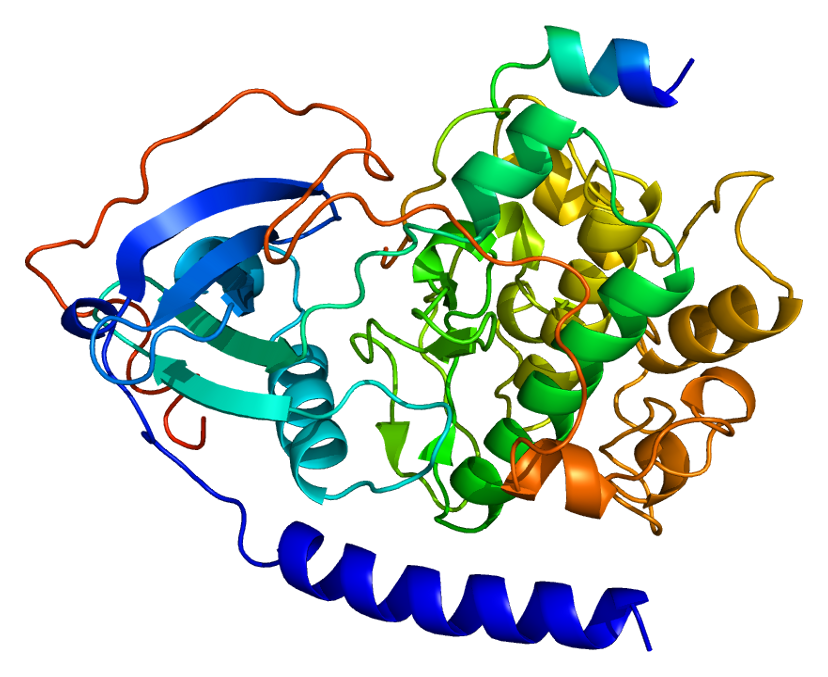
This gene encodes one of the catalytic subunits of protein kinase A, which exists as a tetrameric holoenzyme with two regulatory subunits and two catalytic subunits, in its inactive form. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinase A is important to many cellular processes, including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Constitutive activation of this gene caused either by somatic mutations, or genomic duplications of regions that include this gene, have been associated with hyperplasias and adenomas of the adrenal cortex and are linked to corticotropin-independent Cushing’s syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Tissue-specific isoforms that differ at the N-terminus have been described, and these isoforms may differ in the post-translational modifications that occur at the N-terminus of some isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]
FUNCTION
- Nucleotide binding
- Enables magnesium ion binding
- Enables protein kinase activity
- Enables protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- Enables AMP-activated protein kinase activity
LOCALIZATION
- Located in acrosomal vesicle
- Located in nucleus
- Located in nucleoplasm
- Located in cytoplasm
- Located in mitochondrion
PATHWAYS & INTERACTION
- Involved in mesoderm formation
- Involved in neural tube closure
- Involved in regulation of heart rate
- Involved in renal water homeostasis
- Involved in mRNA processing
- Abnormality of body height
- Autosomal dominant inheritance
- Abnormality of the genital system
- Abnormality of reproductive system physiology
- Tall stature
- Abnormality of the genitourinary system
- Hypogonadism
- Abnormality of head or neck
- Abnormality of the mouth
- Abnormal lip morphology
- Abnormal oral cavity morphology
- Abnormality of the dentition
- Abnormality of upper lip
- Abnormal oral frenulum morphology
- Accessory oral frenulum
- Abnormality of the head
- Abnormality of the face
- Long face
- Abnormality of the philtrum
- Abnormality of the midface
- Short philtrum
- Abnormality of the maxilla
- Hypoplasia of the maxilla
- Abnormality of the musculoskeletal system
- Abnormality of the nose
- Abnormality of the nasal tip
- Tooth malposition
PRKACA Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
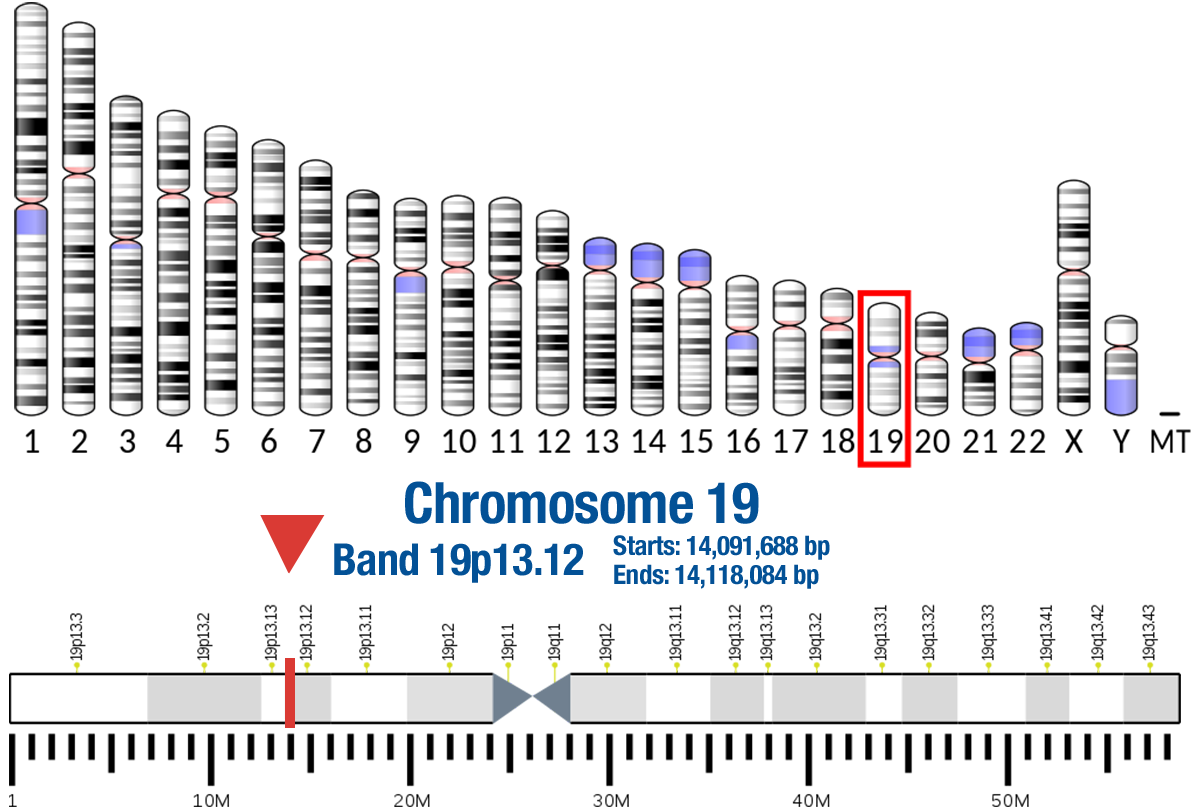
Gene Location