The protein encoded by this gene is part of a complex of proteins that constitute adherens junctions (AJs). AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial cell layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion between cells. The encoded protein also anchors the actin cytoskeleton and may be responsible for transmitting the contact inhibition signal that causes cells to stop dividing once the epithelial sheet is complete. Finally, this protein binds to the product of the APC gene, which is mutated in adenomatous polyposis of the colon. Mutations in this gene are a cause of colorectal cancer (CRC), pilomatrixoma (PTR), medulloblastoma (MDB), and ovarian cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]
Tumor type associations:
- Bladder
- Cervical
- Colorectal
- Endometrial
- Gastric
- Liver
- Melanoma
- Ovarian
- Pancreatic
- Prostate
- Enables transcription coregulator binding
- Enables chromatin binding
- Enables transcription coactivator activity
- Enables protein binding
- Enables beta-catenin binding
- Located in euchromatin
- Located in spindle pole
- Located in nucleus
- Located in nucleoplasm
- Part of transcription regulator complex
- Involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- Involved in protein polyubiquitination
- Involved in embryonic axis specification
- Involved in cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
- Skeletal system development
Key downstream component of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway (PubMed:17524503, PubMed:18077326, PubMed:18086858, PubMed:18957423, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:22155184, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:22699938). In the absence of Wnt, forms a complex with AXIN1, AXIN2, APC, CSNK1A1 and GSK3B that promotes phosphorylation on N-terminal Ser and Thr residues and ubiquitination of CTNNB1 via BTRC and its subsequent degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:17524503, PubMed:18077326, PubMed:18086858, PubMed:18957423, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:22155184, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:22699938). In the presence of Wnt ligand, CTNNB1 is not ubiquitinated and accumulates in the nucleus, where it acts as a coactivator for transcription factors of the TCF/LEF family, leading to activate Wnt responsive genes (PubMed:17524503, PubMed:18077326, PubMed:18086858, PubMed:18957423, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:22155184, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:22699938). Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion, as component of an E-cadherin:catenin adhesion complex (By similarity). Acts as a negative regulator of centrosome cohesion (PubMed:18086858). Involved in the CDK2/PTPN6/CTNNB1/CEACAM1 pathway of insulin internalization (PubMed:21262353). Blocks anoikis of malignant kidney and intestinal epithelial cells and promotes their anchorage-independent growth by down-regulating DAPK2 (PubMed:18957423). Disrupts PML function and PML-NB formation by inhibiting RANBP2-mediated sumoylation of PML (PubMed:22155184). Promotes neurogenesis by maintaining sympathetic neuroblasts within the cell cycle (By similarity). Involved in chondrocyte differentiation via interaction with SOX9: SOX9-binding competes with the binding sites of TCF/LEF within CTNNB1, thereby inhibiting the Wnt signaling (By similarity). CTNB1_HUMAN,P35222
- Pilomatrixoma
- Colorectal Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Medulloblastoma
- Neurodevelopmental Disorder With Spastic Diplegia And Visual Defects
- Exudative Vitreoretinopathy 7
- Severe Intellectual Disability-Progressive Spastic Diplegia Syndrome
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hepatoblastoma
- Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma
- Craniopharyngioma
- Desmoid Tumor
- Gallbladder Cancer
- Exudative Vitreoretinopathy 1
- Melanoma
- Exudative Vitreoretinopathy
- Microcystic Stromal Tumor
- Adenoma
CTNNB1 localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
The protein encoded by this gene is part of a complex of proteins that constitute adherens junctions (AJs). AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial cell layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion between cells. The encoded protein also anchors the actin cytoskeleton and may be responsible for transmitting the contact inhibition signal that causes cells to stop dividing once the epithelial sheet is complete. Finally, this protein binds to the product of the APC gene, which is mutated in adenomatous polyposis of the colon. Mutations in this gene are a cause of colorectal cancer (CRC), pilomatrixoma (PTR), medulloblastoma (MDB), and ovarian cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]
Tumor type associations:
- Bladder
- Cervical
- Colorectal
- Endometrial
- Gastric
- Liver
- Melanoma
- Ovarian
- Pancreatic
- Prostate
- Enables transcription coregulator binding
- Enables chromatin binding
- Enables transcription coactivator activity
- Enables protein binding
- Enables beta-catenin binding
- Located in euchromatin
- Located in spindle pole
- Located in nucleus
- Located in nucleoplasm
- Part of transcription regulator complex
- Involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- Involved in protein polyubiquitination
- Involved in embryonic axis specification
- Involved in cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation
- Skeletal system development
Key downstream component of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway (PubMed:17524503, PubMed:18077326, PubMed:18086858, PubMed:18957423, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:22155184, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:22699938). In the absence of Wnt, forms a complex with AXIN1, AXIN2, APC, CSNK1A1 and GSK3B that promotes phosphorylation on N-terminal Ser and Thr residues and ubiquitination of CTNNB1 via BTRC and its subsequent degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:17524503, PubMed:18077326, PubMed:18086858, PubMed:18957423, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:22155184, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:22699938). In the presence of Wnt ligand, CTNNB1 is not ubiquitinated and accumulates in the nucleus, where it acts as a coactivator for transcription factors of the TCF/LEF family, leading to activate Wnt responsive genes (PubMed:17524503, PubMed:18077326, PubMed:18086858, PubMed:18957423, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:22155184, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:22699938). Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion, as component of an E-cadherin:catenin adhesion complex (By similarity). Acts as a negative regulator of centrosome cohesion (PubMed:18086858). Involved in the CDK2/PTPN6/CTNNB1/CEACAM1 pathway of insulin internalization (PubMed:21262353). Blocks anoikis of malignant kidney and intestinal epithelial cells and promotes their anchorage-independent growth by down-regulating DAPK2 (PubMed:18957423). Disrupts PML function and PML-NB formation by inhibiting RANBP2-mediated sumoylation of PML (PubMed:22155184). Promotes neurogenesis by maintaining sympathetic neuroblasts within the cell cycle (By similarity). Involved in chondrocyte differentiation via interaction with SOX9: SOX9-binding competes with the binding sites of TCF/LEF within CTNNB1, thereby inhibiting the Wnt signaling (By similarity). CTNB1_HUMAN,P35222
- Pilomatrixoma
- Colorectal Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Medulloblastoma
- Neurodevelopmental Disorder With Spastic Diplegia And Visual Defects
- Exudative Vitreoretinopathy 7
- Severe Intellectual Disability-Progressive Spastic Diplegia Syndrome
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hepatoblastoma
- Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma
- Craniopharyngioma
- Desmoid Tumor
- Gallbladder Cancer
- Exudative Vitreoretinopathy 1
- Melanoma
- Exudative Vitreoretinopathy
- Microcystic Stromal Tumor
- Adenoma
CTNNB1 localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
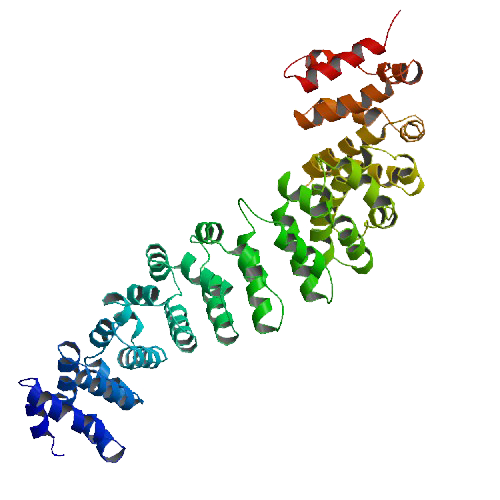
Three-dimensional structure of the armadillo repeat region of beta-catenin. Huber, A.H., Nelson, W.J., Weis, W.I. Journal: (1997) Cell(Cambridge,Mass.) 90: 871-882. Link.
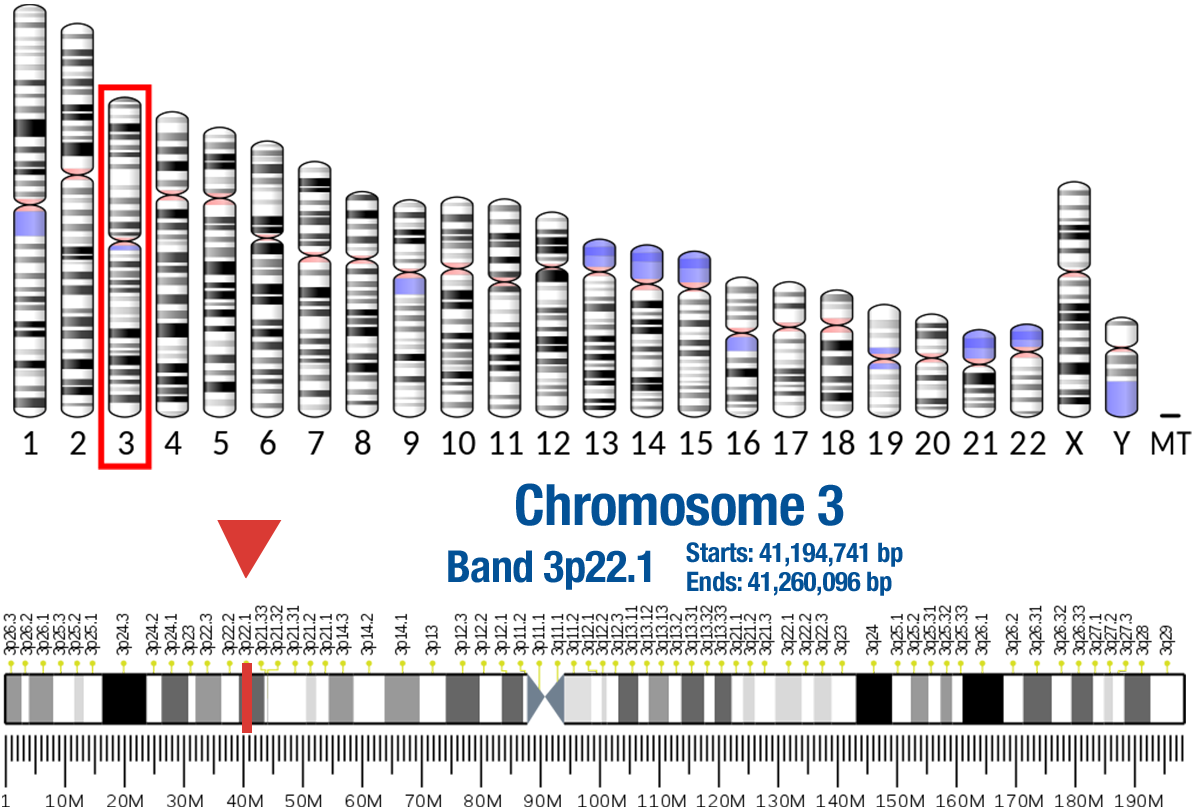
Gene Location