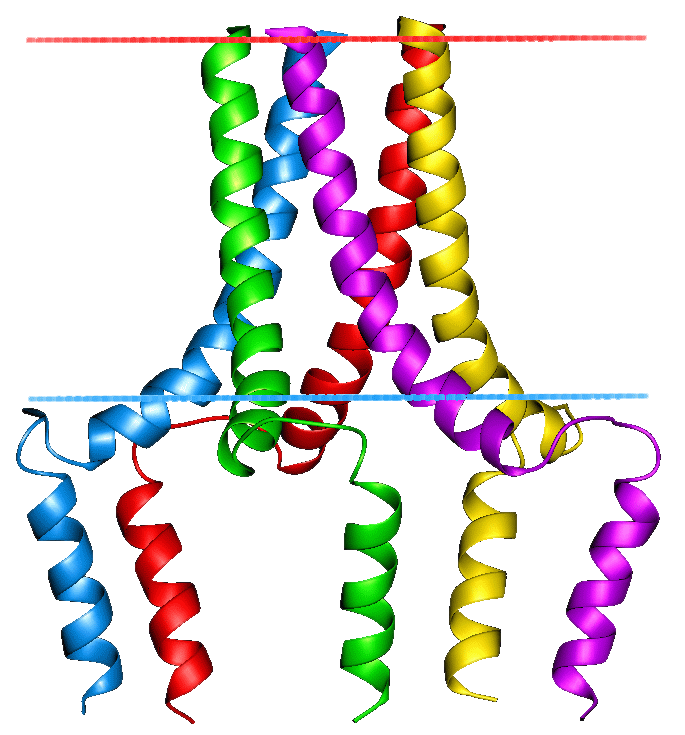
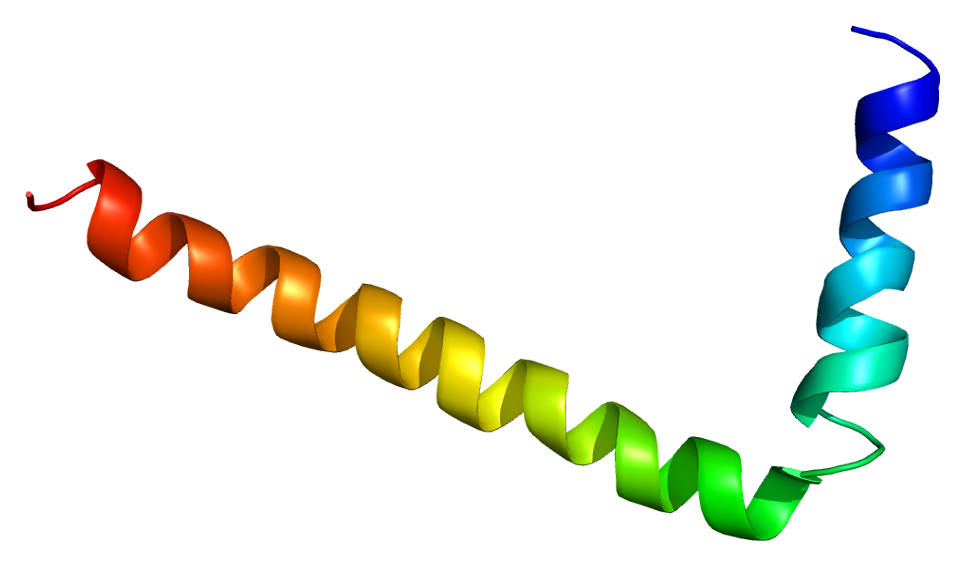The protein encoded by this gene is found as a pentamer and is a major substrate for the cAMP-dependent protein kinase in cardiac muscle. The encoded protein is an inhibitor of cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase in the unphosphorylated state, but inhibition is relieved upon phosphorylation of the protein. The subsequent activation of the Ca(2+) pump leads to enhanced muscle relaxation rates, thereby contributing to the inotropic response elicited in heart by beta-agonists. The encoded protein is a key regulator of cardiac diastolic function. Mutations in this gene are a cause of inherited human dilated cardiomyopathy with refractory congestive heart failure, and also familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]
- Regulation of the force of heart contraction
- Calcium ion transport
- Cellular calcium ion homeostasis
- Notch signaling pathway
- Blood circulation
- Cardiomyopathy, dilated, 1p
- Cardiomyopathy, familial hypertrophic, 18
- Cardiac arrest
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, familial, 9
Gene Location