
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP contains two tandem Src homology-2 domains, which function as phospho-tyrosine binding domains and mediate the interaction of this PTP with its substrates. This PTP is widely expressed in most tissues and plays a regulatory role in various cell signaling events that are important for a diversity of cell functions, such as mitogenic activation, metabolic control, transcription regulation, and cell migration. Mutations in this gene are a cause of Noonan syndrome as well as acute myeloid leukemia. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]
- DNA damage checkpoint
- Activation of MAPK activity
- Protein dephosphorylation
- Lipid metabolic process
- Triglyceride metabolic process
- Noonan syndrome 1
- Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia
- Metachondromatosis
- Leopard syndrome 1
- Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Noonan Syndrome
- General Cardiomyopathy
Based on Ayass Bioscience, LLC Data Analysis
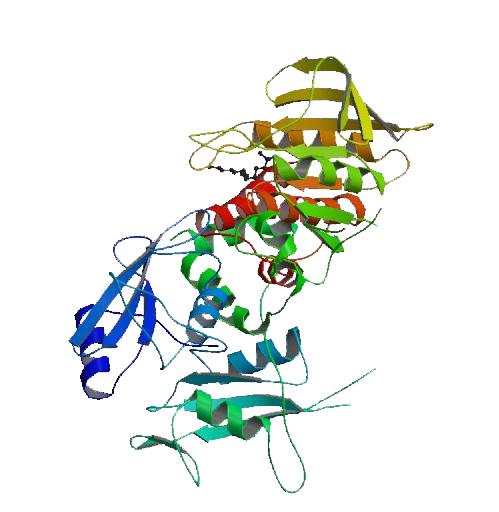
Crystal structure of PTPN11 (Shp-2), 525 total residues. Hof, P., Pluskey, S., Dhe-Paganon, S., Eck, M.J., Shoelson, S.E. – Protein Data Bank.
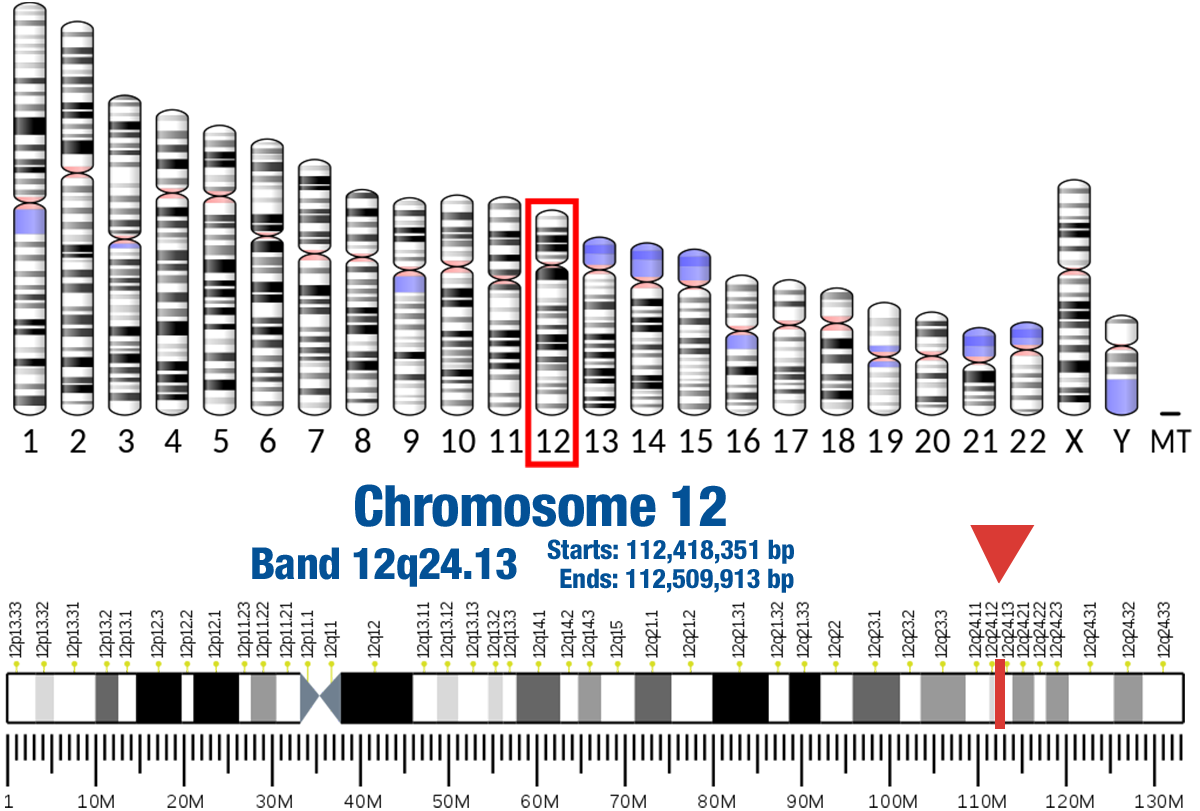
Gene Location
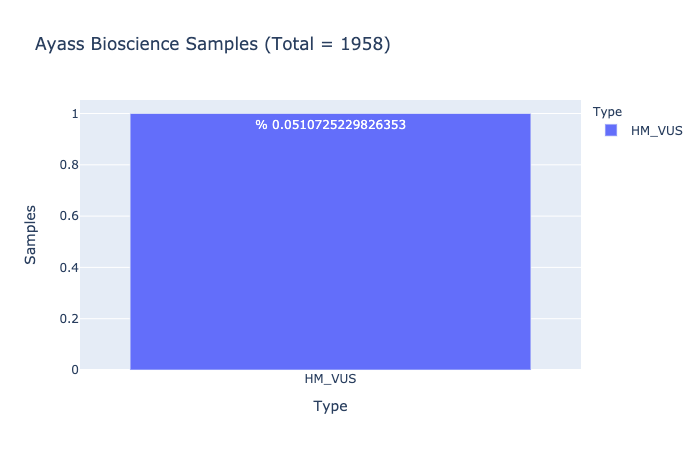
HM-VUS Prevalence
% 0.0510725229826353
Ratio of samples with at least 1 High/Med VUS variant (Computed from Ayass Bioscience Samples)
High/Med VUS Variants
T=0.000004(1/251186,GnomAD_exome)
T=0.000008(1/121412,ExAC)
T=0.00000(0/78684,PAGE_STUDY)
T=0.0000(0/6578,ALFAProject)

