
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the MRP subfamily which is involved in multi-drug resistance. This protein is thought to form ATP-sensitive potassium channels in cardiac, skeletal, and vascular and non-vascular smooth muscle. Protein structure suggests a role as the drug-binding channel-modulating subunit of the extra-pancreatic ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Mutations in this gene are associated with cardiomyopathy dilated type 1O. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2011]
- Potassium ion transport
- Response to ATP
- Defense response to virus
- Transmembrane transport
- Cardiac conduction
- Cantu syndrome
- Cardiomyopathy, dilated, 1o
- Atrial fibrillation, familial, 12
- Acromegaloid hypertrichosis syndrome
- Acromegaloid facial appearance syndrome
- General Cardiomyopathy
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- General Arrhythmia
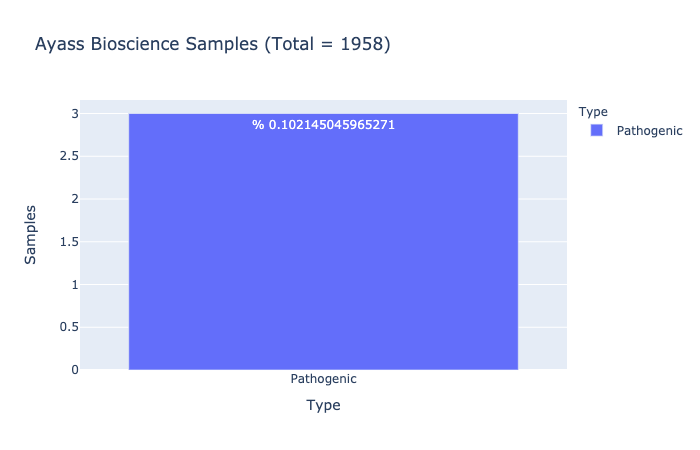
Based on Ayass Bioscience, LLC Data Analysis
ABCC9 localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
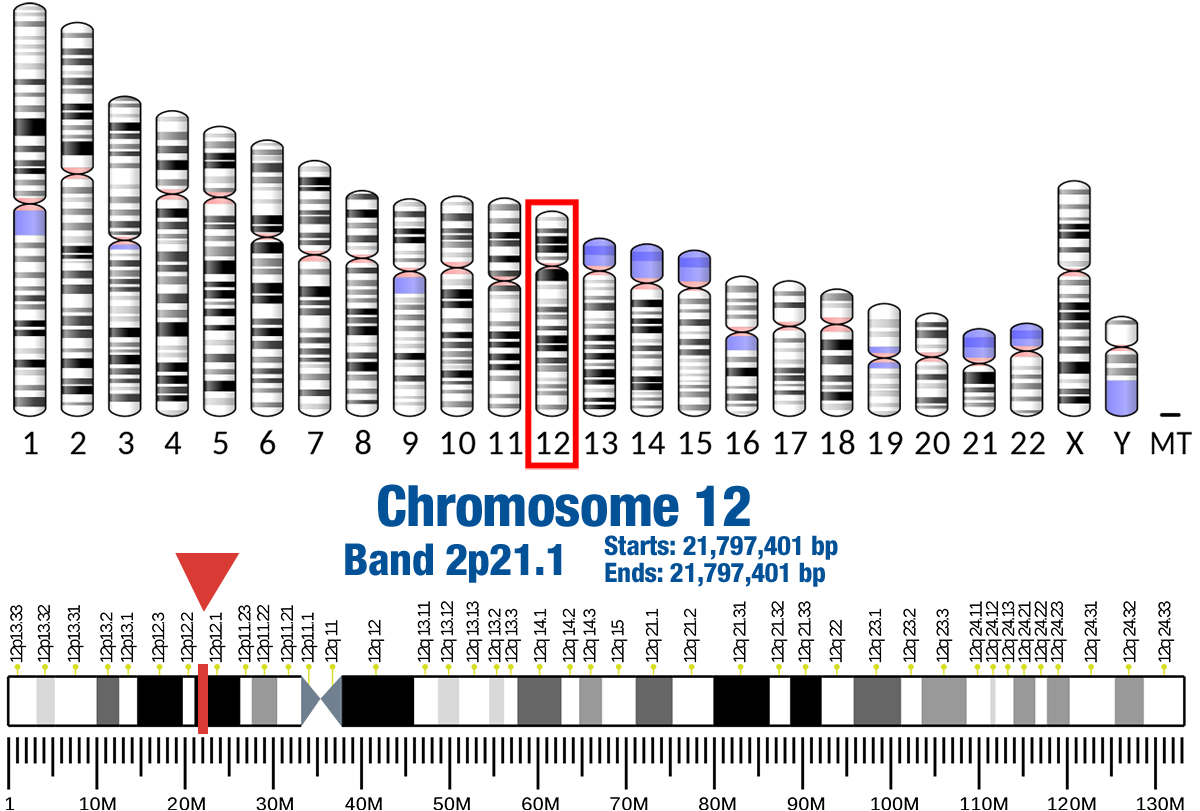
Gene Location
Pathogenic Prevalence
% 0.102145045965271
Ratio of samples with at least 1 pathogenic variant (Computed from Ayass Bioscience Samples)
Pathogenic Variants
insA=0.00040(5/12518,GO-ESP)
insA=0.0005(2/3854,ALSPAC)
insA=0.0008(3/3708,TWINSUK)

