The product encoded by this gene belongs to the actin family of proteins, which are highly conserved proteins that play a role in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha, beta and gamma actin isoforms have been identified, with alpha actins being a major constituent of the contractile apparatus, while beta and gamma actins are involved in the regulation of cell motility. This actin is an alpha actin that is found in skeletal muscle. Mutations in this gene cause a variety of myopathies, including nemaline myopathy, congenital myopathy with excess of thin myofilaments, congenital myopathy with cores, and congenital myopathy with fiber-type disproportion, diseases that lead to muscle fiber defects with manifestations such as hypotonia. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2019]
- Muscle contraction
- Response to mechanical stimulus
- Response to extracellular stimulus
- Response to lithium ion
- Positive regulation of gene expression
- Myopathy, scapulohumeroperoneal
- Nemaline myopathy 3
- Congenital fiber-type disproportion
- Myopathy, congenital, with fiber-type disproportion
- Zebra body myopathy
- General Cardiomyopathy
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Based on Ayass Bioscience, LLC Data Analysis
ACTA1 Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
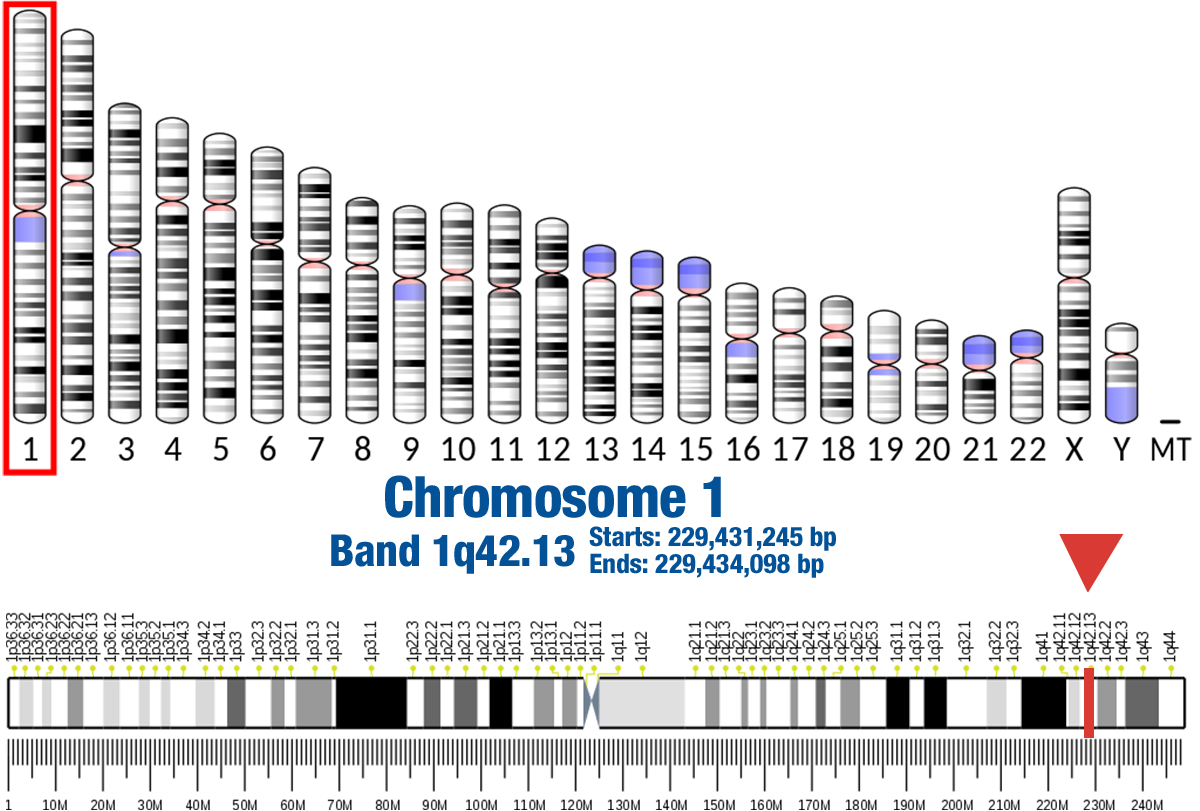
Gene Location
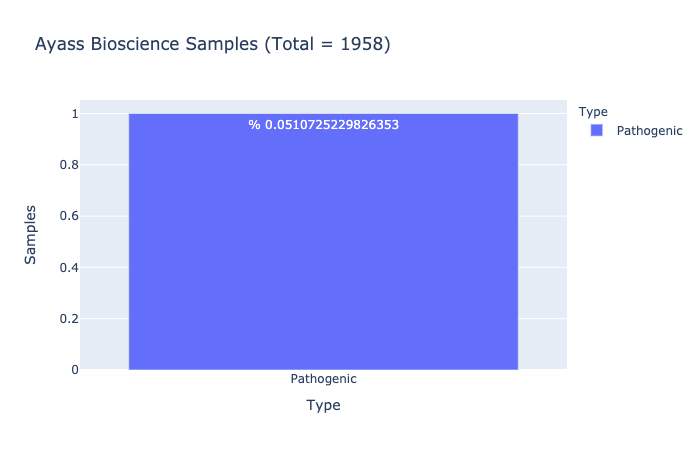
Pathogenic Prevalence
% 0.0510725229826353
Ratio of samples with at least 1 pathogenic variant (Computed from Ayass Bioscience Samples)