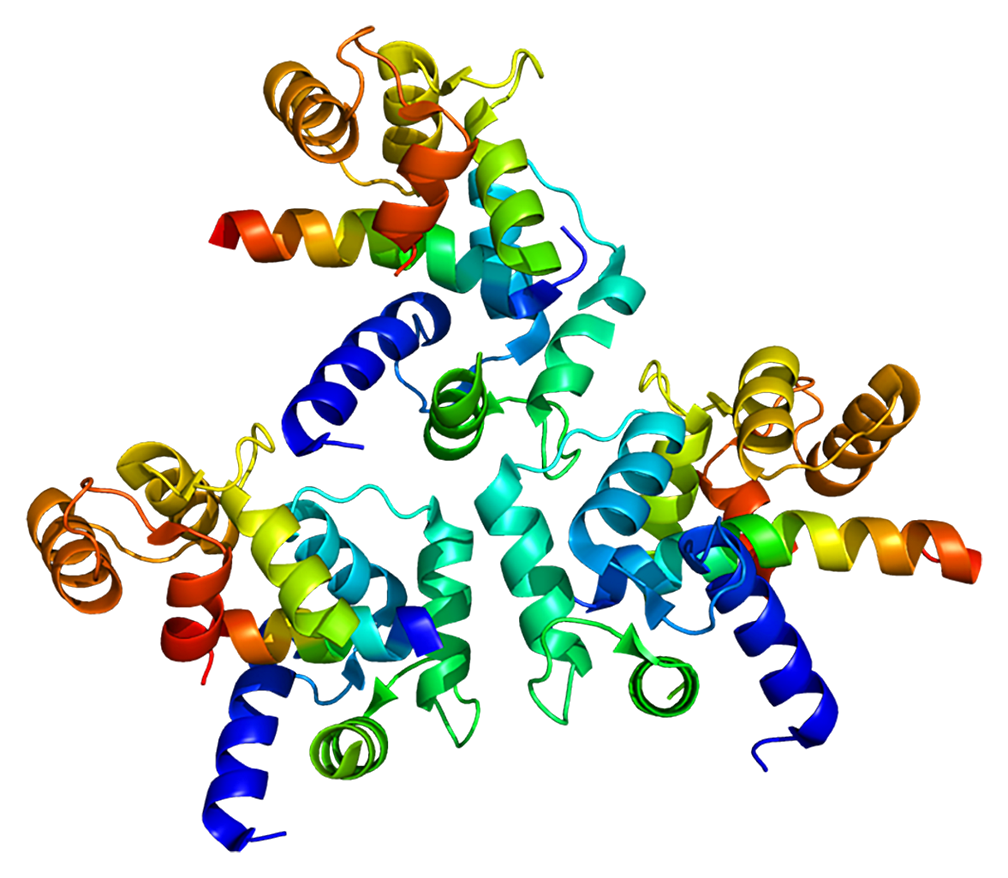
This gene encodes an alpha-1 subunit of a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions into the cell upon membrane polarization. The alpha-1 subunit consists of 24 transmembrane segments and forms the pore through which ions pass into the cell. The calcium channel consists of a complex of alpha-1, alpha-2/delta, beta, and gamma subunits in a 1:1:1:1 ratio. There are multiple isoforms of each of these proteins, either encoded by different genes or the result of alternative splicing of transcripts. The protein encoded by this gene binds to and is inhibited by dihydropyridine. Alternative splicing results in many transcript variants encoding different proteins. Some of the predicted proteins may not produce functional ion channel subunits. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2012]
- Immune system development
- Ion transport
- Calcium ion transport
- Positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration
- Heart development
- Timothy syndrome
- Long qt syndrome 8
- Brugada syndrome 3
- Brugada syndrome
- Ventricular fibrillation, paroxysmal familial, 1
- General Arrhythmia
- Long QT
- Brugada Syndrome
- Cardiomuscular
Based on Ayass Bioscience, LLC Data Analysis
CACNA1C localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
Gene Location
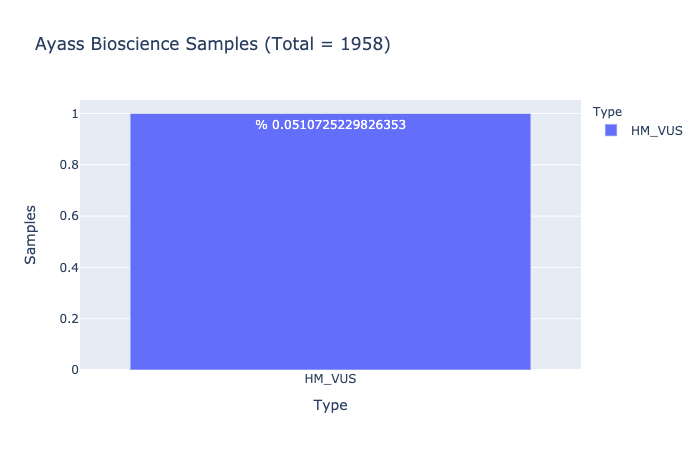
HM-VUS Prevalence
% 0.0510725229826353
Ratio of samples with at least 1 High/Med VUS variant (Computed from Ayass Bioscience Samples)
High/Med VUS Variants
G=0.000358(45/125568,TOPMED)
G=0.00000(0/85990,ALFAProject)
G=0.00052(41/78702,PAGE_STUDY)
G=0.00019(8/42540,ExAC)
G=0.00019(6/31406,GnomAD)
G=0.00016(2/12352,GO-ESP)