This gene is a proto-oncogene that encodes a RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligase. The encoded protein is one of the enzymes required for targeting substrates for degradation by the proteasome. This protein mediates the transfer of ubiquitin from ubiquitin conjugating enzymes (E2) to specific substrates. This protein also contains an N-terminal phosphotyrosine binding domain that allows it to interact with numerous tyrosine-phosphorylated substrates and target them for proteasome degradation. As such it functions as a negative regulator of many signal transduction pathways. This gene has been found to be mutated or translocated in many cancers including acute myeloid leukaemia, and expansion of CGG repeats in the 5′ UTR has been associated with Jacobsen syndrome. Mutations in this gene are also the cause of Noonan syndrome-like disorder. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]
- Enables phosphotyrosine residue binding
- Enables ubiquitin-protein transferase activity
- Enables calcium ion binding
- Enables protein binding
- Transferase activity
- Cytoplasm
- Located in Golgi apparatus
- Located in cytosol
- Located in plasma membrane
- Located in focal adhesion
- Involved in protein polyubiquitination
- Involved in ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process
- Involved in protein monoubiquitination
- Involved in cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
- Involved in signal transduction
Adapter protein that functions as a negative regulator of many signaling pathways that are triggered by activation of cell surface receptors. Acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, which accepts ubiquitin from specific E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, and then transfers it to substrates promoting their degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:17094949). Ubiquitinates SPRY2 (PubMed:17094949, PubMed:17974561). Ubiquitinates EGFR (PubMed:17974561). Recognizes activated receptor tyrosine kinases, including KIT, FLT1, FGFR1, FGFR2, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, CSF1R, EPHA8 and KDR and terminates signaling. Recognizes membrane-bound HCK, SRC and other kinases of the SRC family and mediates their ubiquitination and degradation. Participates in signal transduction in hematopoietic cells. Plays an important role in the regulation of osteoblast differentiation and apoptosis. Essential for osteoclastic bone resorption. The ‘Tyr-731’ phosphorylated form induces the activation and recruitment of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to the cell membrane in a signaling pathway that is critical for osteoclast function. May be functionally coupled with the E2 ubiquitin-protein ligase UB2D3. In association with CBLB, required for proper feedback inhibition of ciliary platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha (PDGFRA) signaling pathway via ubiquitination and internalization of PDGFRA (By similarity).
- Noonan Syndrome-Like Disorder With Or Without Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia
- Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia
- Fragile Site 11b
- Pseudo-Turner Syndrome
- Noonan Syndrome And Noonan-Related Syndrome
- Noonan Syndrome 1
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis
- Rasopathy
- Ovarian Germ Cell Cancer
- Jacobsen Syndrome
- Hematologic Cancer
- Thanatophoric Dysplasia, Type I
- Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome
- Core Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
- General Cardiomyopathy
- Noonan Syndrome
Based on Ayass Bioscience, LLC Data Analysis
CBL Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
This gene is a proto-oncogene that encodes a RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligase. The encoded protein is one of the enzymes required for targeting substrates for degradation by the proteasome. This protein mediates the transfer of ubiquitin from ubiquitin conjugating enzymes (E2) to specific substrates. This protein also contains an N-terminal phosphotyrosine binding domain that allows it to interact with numerous tyrosine-phosphorylated substrates and target them for proteasome degradation. As such it functions as a negative regulator of many signal transduction pathways. This gene has been found to be mutated or translocated in many cancers including acute myeloid leukaemia, and expansion of CGG repeats in the 5′ UTR has been associated with Jacobsen syndrome. Mutations in this gene are also the cause of Noonan syndrome-like disorder. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]
- Enables phosphotyrosine residue binding
- Enables ubiquitin-protein transferase activity
- Enables calcium ion binding
- Enables protein binding
- Transferase activity
- Cytoplasm
- Located in Golgi apparatus
- Located in cytosol
- Located in plasma membrane
- Located in focal adhesion
- Involved in protein polyubiquitination
- Involved in ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process
- Involved in protein monoubiquitination
- Involved in cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
- Involved in signal transduction
Adapter protein that functions as a negative regulator of many signaling pathways that are triggered by activation of cell surface receptors. Acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, which accepts ubiquitin from specific E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, and then transfers it to substrates promoting their degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:17094949). Ubiquitinates SPRY2 (PubMed:17094949, PubMed:17974561). Ubiquitinates EGFR (PubMed:17974561). Recognizes activated receptor tyrosine kinases, including KIT, FLT1, FGFR1, FGFR2, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, CSF1R, EPHA8 and KDR and terminates signaling. Recognizes membrane-bound HCK, SRC and other kinases of the SRC family and mediates their ubiquitination and degradation. Participates in signal transduction in hematopoietic cells. Plays an important role in the regulation of osteoblast differentiation and apoptosis. Essential for osteoclastic bone resorption. The ‘Tyr-731’ phosphorylated form induces the activation and recruitment of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to the cell membrane in a signaling pathway that is critical for osteoclast function. May be functionally coupled with the E2 ubiquitin-protein ligase UB2D3. In association with CBLB, required for proper feedback inhibition of ciliary platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha (PDGFRA) signaling pathway via ubiquitination and internalization of PDGFRA (By similarity).
- Noonan Syndrome-Like Disorder With Or Without Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia
- Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia
- Fragile Site 11b
- Pseudo-Turner Syndrome
- Noonan Syndrome And Noonan-Related Syndrome
- Noonan Syndrome 1
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis
- Rasopathy
- Ovarian Germ Cell Cancer
- Jacobsen Syndrome
- Hematologic Cancer
- Thanatophoric Dysplasia, Type I
- Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome
- Core Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
- General Cardiomyopathy
- Noonan Syndrome
Based on Ayass Bioscience, LLC Data Analysis
CBL Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
Gene Location

HM-VUS Prevalence
% 0.102145045965271
Ratio of samples with at least 1 High/Med VUS variant (Computed from Ayass Bioscience Samples)
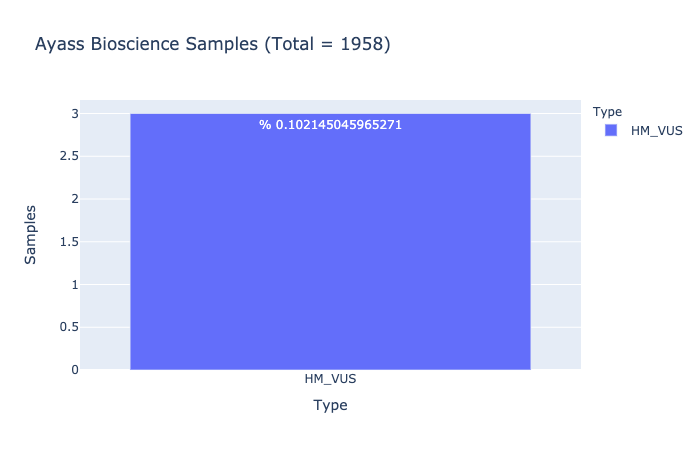
High/Med VUS Variants
T=0.000060(15/251364,GnomAD_exome)
T=0.000072(9/125568,TOPMED)
T=0.000066(8/120674,ExAC)
T=0.00019(17/88598,ALFAProject)
T=0.00010(8/78696,PAGE_STUDY)
T=0.00013(4/31398,GnomAD)
T=0.00023(3/12988,GO-ESP)