
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28 and S. pombe cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. The activity of this kinase is restricted to the G1-S phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16(INK4a). This kinase was shown to be responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product (Rb). Mutations in this gene as well as in its related proteins including D-type cyclins, p16(INK4a) and Rb were all found to be associated with tumorigenesis of a variety of cancers. Multiple polyadenylation sites of this gene have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- Nucleotide binding
- Protein kinase activity
- Protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- Enables cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- Protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity
- Part of cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex
- Located in chromatin
- Located in nucleus
- Located in nucleoplasm
- Part of transcription regulator complex
- Involved in G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle
- Involved in protein phosphorylation
- Cell cycle
- Involved in signal transduction
- Involved in positive regulation of cell population proliferation
Ser/Thr-kinase component of cyclin D-CDK4 (DC) complexes that phosphorylate and inhibit members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulate the cell-cycle during G(1)/S transition. Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociation of the transcription factor E2F from the RB/E2F complexes and the subsequent transcription of E2F target genes which are responsible for the progression through the G(1) phase. Hypophosphorylates RB1 in early G(1) phase. Cyclin D-CDK4 complexes are major integrators of various mitogenenic and antimitogenic signals. Also phosphorylates SMAD3 in a cell-cycle-dependent manner and represses its transcriptional activity. Component of the ternary complex, cyclin D/CDK4/CDKN1B, required for nuclear translocation and activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex. CDK4_HUMAN,P11802
- Melanoma, Cutaneous Malignant 3
- Hereditary Melanoma
- Melanoma, Cutaneous Malignant 1
- Inherited Cancer-Predisposing Syndrome
- Tumor Predisposition Syndrome
- Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma
- Well-Differentiated Liposarcoma
- Retinoblastoma
- Parosteal Osteosarcoma
- Melanoma
- Skin Melanoma
- Undifferentiated Embryonal Sarcoma Of The Liver
- Myxoid Liposarcoma
- Plasma Cell Neoplasm
- Skin Carcinoma
- Ring Chromosome 7
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma
- Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma
- Mixed Liposarcoma
- Lung Cancer
- B-Cell Lymphoma
CDK4 Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28 and S. pombe cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. The activity of this kinase is restricted to the G1-S phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16(INK4a). This kinase was shown to be responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product (Rb). Mutations in this gene as well as in its related proteins including D-type cyclins, p16(INK4a) and Rb were all found to be associated with tumorigenesis of a variety of cancers. Multiple polyadenylation sites of this gene have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- Nucleotide binding
- Protein kinase activity
- Protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- Enables cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- Protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity
- Part of cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex
- Located in chromatin
- Located in nucleus
- Located in nucleoplasm
- Part of transcription regulator complex
- Involved in G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle
- Involved in protein phosphorylation
- Cell cycle
- Involved in signal transduction
- Involved in positive regulation of cell population proliferation
Ser/Thr-kinase component of cyclin D-CDK4 (DC) complexes that phosphorylate and inhibit members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulate the cell-cycle during G(1)/S transition. Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociation of the transcription factor E2F from the RB/E2F complexes and the subsequent transcription of E2F target genes which are responsible for the progression through the G(1) phase. Hypophosphorylates RB1 in early G(1) phase. Cyclin D-CDK4 complexes are major integrators of various mitogenenic and antimitogenic signals. Also phosphorylates SMAD3 in a cell-cycle-dependent manner and represses its transcriptional activity. Component of the ternary complex, cyclin D/CDK4/CDKN1B, required for nuclear translocation and activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex. CDK4_HUMAN,P11802
- Melanoma, Cutaneous Malignant 3
- Hereditary Melanoma
- Melanoma, Cutaneous Malignant 1
- Inherited Cancer-Predisposing Syndrome
- Tumor Predisposition Syndrome
- Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma
- Well-Differentiated Liposarcoma
- Retinoblastoma
- Parosteal Osteosarcoma
- Melanoma
- Skin Melanoma
- Undifferentiated Embryonal Sarcoma Of The Liver
- Myxoid Liposarcoma
- Plasma Cell Neoplasm
- Skin Carcinoma
- Ring Chromosome 7
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma
- Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma
- Mixed Liposarcoma
- Lung Cancer
- B-Cell Lymphoma
CDK4 Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
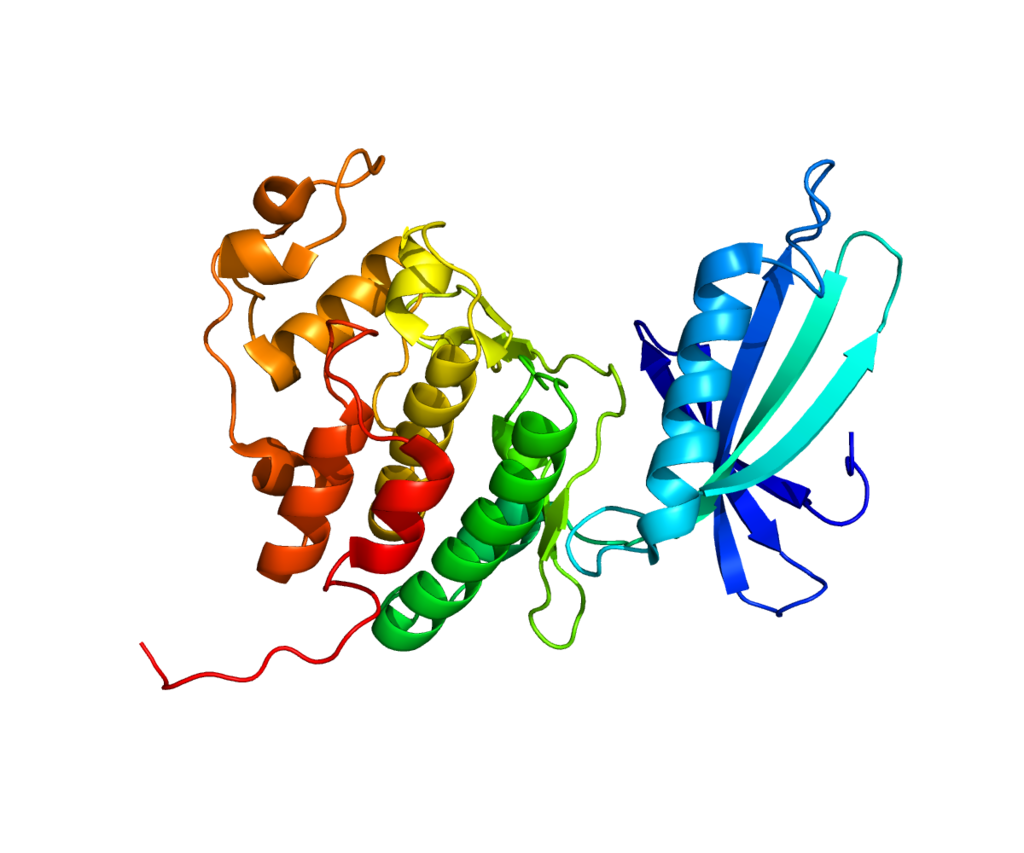
Pleiotrope. Structure of protein CDK4.Based on PyMOL rendering of PDB 1LD2.
Gene Location


