This gene encodes an estrogen receptor and ligand-activated transcription factor. The canonical protein contains an N-terminal ligand-independent transactivation domain, a central DNA binding domain, a hinge domain, and a C-terminal ligand-dependent transactivation domain. The protein localizes to the nucleus where it may form either a homodimer or a heterodimer with estrogen receptor 2. The protein encoded by this gene regulates the transcription of many estrogen-inducible genes that play a role in growth, metabolism, sexual development, gestation, and other reproductive functions and is expressed in many non-reproductive tissues. The receptor encoded by this gene plays a key role in breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and osteoporosis. This gene is reported to have dozens of transcript variants due to the use of alternate promoters and alternative splicing, however, the full-length nature of many of these variants remain uncertain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]
- Enables RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- Enables DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- Enables TFIIB-class transcription factor binding
- Enables transcription coregulator binding
- Enables transcription corepressor binding
- Located in chromatin
- located in euchromatin
- Located in nucleus
- Located in nucleoplasm
- Part of transcription regulator complex
- Involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- Involved in antral ovarian follicle growth
- Involved in epithelial cell development
- Involved in chromatin remodeling
- Involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3 (PubMed:17922032). ESR1_HUMAN,P03372
- Estrogen Resistance
- Breast Cancer
- Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita 3, Myogenic Type
- Myocardial Infarction
- Migraine With Or Without Aura 1
- Osteoporosis
- Breast Disease
- Breast Ductal Carcinoma
- Myoma
- Endometrial Hyperplasia
- Estrogen-Receptor Negative Breast Cancer
- Migraine Without Aura
- Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma
- Progesterone-Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
- Postmenopausal Atrophic Vaginitis
- Estrogen-Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
- Vulvar Syringoma
- Endometrial Disease
- Female Breast Cancer
- Vaginitis
- In Situ Carcinoma
- Leiomyoma
- Endometrial Cancer
- Lobular Neoplasia
- Adenomyosis
- Intravenous Leiomyomatosis
- Breast Fibroadenoma
- Gynecomastia
- Bone Cancer
ESR1 Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
This gene encodes an estrogen receptor and ligand-activated transcription factor. The canonical protein contains an N-terminal ligand-independent transactivation domain, a central DNA binding domain, a hinge domain, and a C-terminal ligand-dependent transactivation domain. The protein localizes to the nucleus where it may form either a homodimer or a heterodimer with estrogen receptor 2. The protein encoded by this gene regulates the transcription of many estrogen-inducible genes that play a role in growth, metabolism, sexual development, gestation, and other reproductive functions and is expressed in many non-reproductive tissues. The receptor encoded by this gene plays a key role in breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and osteoporosis. This gene is reported to have dozens of transcript variants due to the use of alternate promoters and alternative splicing, however, the full-length nature of many of these variants remain uncertain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]
- Enables RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- Enables DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- Enables TFIIB-class transcription factor binding
- Enables transcription coregulator binding
- Enables transcription corepressor binding
- Located in chromatin
- located in euchromatin
- Located in nucleus
- Located in nucleoplasm
- Part of transcription regulator complex
- Involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- Involved in antral ovarian follicle growth
- Involved in epithelial cell development
- Involved in chromatin remodeling
- Involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3 (PubMed:17922032). ESR1_HUMAN,P03372
- Estrogen Resistance
- Breast Cancer
- Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita 3, Myogenic Type
- Myocardial Infarction
- Migraine With Or Without Aura 1
- Osteoporosis
- Breast Disease
- Breast Ductal Carcinoma
- Myoma
- Endometrial Hyperplasia
- Estrogen-Receptor Negative Breast Cancer
- Migraine Without Aura
- Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma
- Progesterone-Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
- Postmenopausal Atrophic Vaginitis
- Estrogen-Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
- Vulvar Syringoma
- Endometrial Disease
- Female Breast Cancer
- Vaginitis
- In Situ Carcinoma
- Leiomyoma
- Endometrial Cancer
- Lobular Neoplasia
- Adenomyosis
- Intravenous Leiomyomatosis
- Breast Fibroadenoma
- Gynecomastia
- Bone Cancer
ESR1 Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
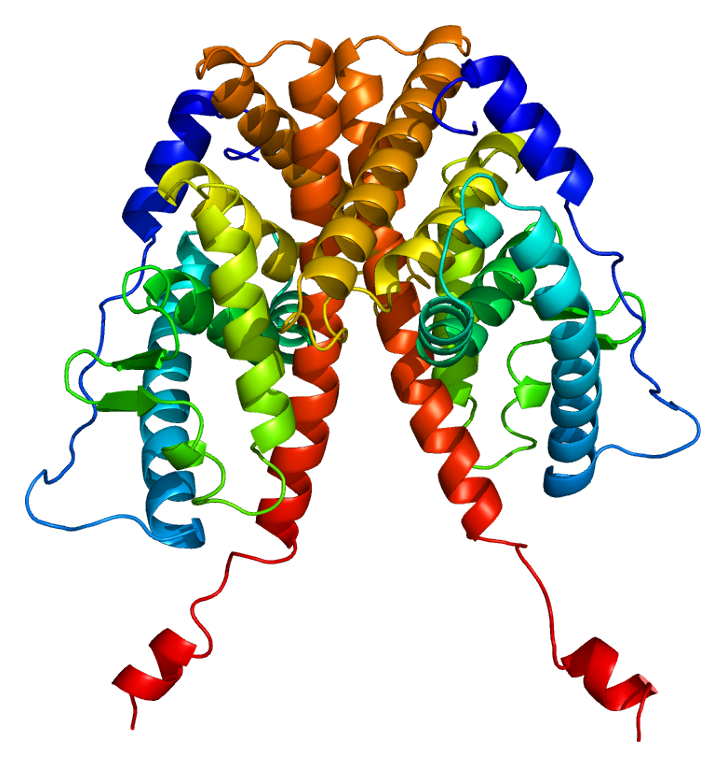
Emw. Structure of the ESR1 protein. Based on PyMOL rendering of PDB 1a52.
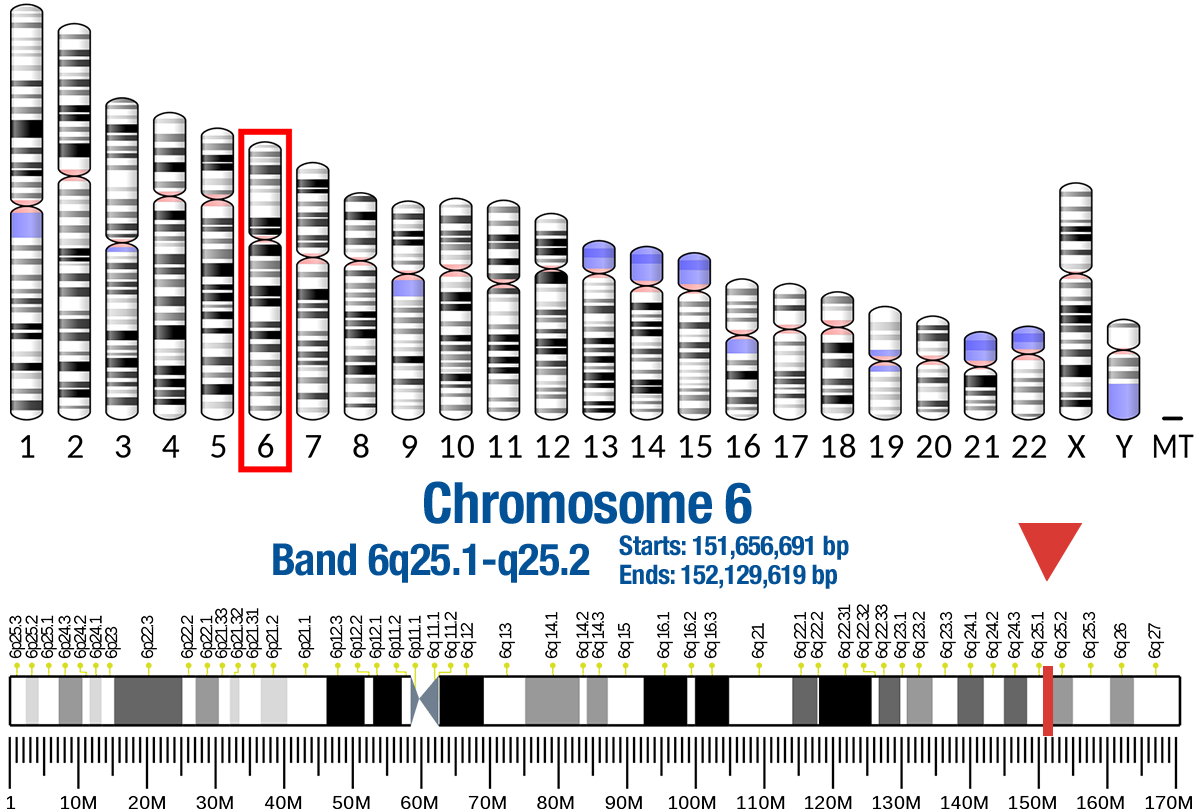
Gene Location