The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family, where amino acid sequence is highly conserved between members and throughout evolution. FGFR family members differ from one another in their ligand affinities and tissue distribution. A full-length representative protein consists of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin-like domains, a single hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion of the protein interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and differentiation. This particular family member binds both acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors and is involved in limb induction. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Pfeiffer syndrome, Jackson-Weiss syndrome, Antley-Bixler syndrome, osteoglophonic dysplasia, and autosomal dominant Kallmann syndrome 2. Chromosomal aberrations involving this gene are associated with stem cell myeloproliferative disorder and stem cell leukemia lymphoma syndrome. Alternatively spliced variants which encode different protein isoforms have been described; however, not all variants have been fully characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- Nucleotide binding
- Protein kinase activity
- Enables protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity
- enables protein tyrosine kinase activity
- enables transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
- Located in extracellular region
- Located in nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Located in cytosol
- Located in plasma membrane
- Involved in MAPK cascade
- Involved in skeletal system development
- Involved in neuron migration
- Involved in epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- Involved in protein phosphorylation
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation and migration. Required for normal mesoderm patterning and correct axial organization during embryonic development, normal skeletogenesis and normal development of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neuronal system. Phosphorylates PLCG1, FRS2, GAB1 and SHB. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Promotes phosphorylation of SHC1, STAT1 and PTPN11/SHP2. In the nucleus, enhances RPS6KA1 and CREB1 activity and contributes to the regulation of transcription. FGFR1 signaling is down-regulated by IL17RD/SEF, and by FGFR1 ubiquitination, internalization and degradation. FGFR1_HUMAN,P11362
Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism 2 With Or Without Anosmia
Chromosome 8p11 Myeloproliferative Syndrome
Rosette-Forming Glioneuronal Tumor
Non-Syndromic Metopic Craniosynostosis
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism 7 With Or Without Anosmia
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism 1 With Or Without Anosmia
FGFR1 Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family, where amino acid sequence is highly conserved between members and throughout evolution. FGFR family members differ from one another in their ligand affinities and tissue distribution. A full-length representative protein consists of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin-like domains, a single hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion of the protein interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and differentiation. This particular family member binds both acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors and is involved in limb induction. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Pfeiffer syndrome, Jackson-Weiss syndrome, Antley-Bixler syndrome, osteoglophonic dysplasia, and autosomal dominant Kallmann syndrome 2. Chromosomal aberrations involving this gene are associated with stem cell myeloproliferative disorder and stem cell leukemia lymphoma syndrome. Alternatively spliced variants which encode different protein isoforms have been described; however, not all variants have been fully characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- Nucleotide binding
- Protein kinase activity
- Enables protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity
- enables protein tyrosine kinase activity
- enables transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
- Located in extracellular region
- Located in nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Located in cytosol
- Located in plasma membrane
- Involved in MAPK cascade
- Involved in skeletal system development
- Involved in neuron migration
- Involved in epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- Involved in protein phosphorylation
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation and migration. Required for normal mesoderm patterning and correct axial organization during embryonic development, normal skeletogenesis and normal development of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neuronal system. Phosphorylates PLCG1, FRS2, GAB1 and SHB. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Promotes phosphorylation of SHC1, STAT1 and PTPN11/SHP2. In the nucleus, enhances RPS6KA1 and CREB1 activity and contributes to the regulation of transcription. FGFR1 signaling is down-regulated by IL17RD/SEF, and by FGFR1 ubiquitination, internalization and degradation. FGFR1_HUMAN,P11362
Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism 2 With Or Without Anosmia
Chromosome 8p11 Myeloproliferative Syndrome
Rosette-Forming Glioneuronal Tumor
Non-Syndromic Metopic Craniosynostosis
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism 7 With Or Without Anosmia
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism 1 With Or Without Anosmia
FGFR1 Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
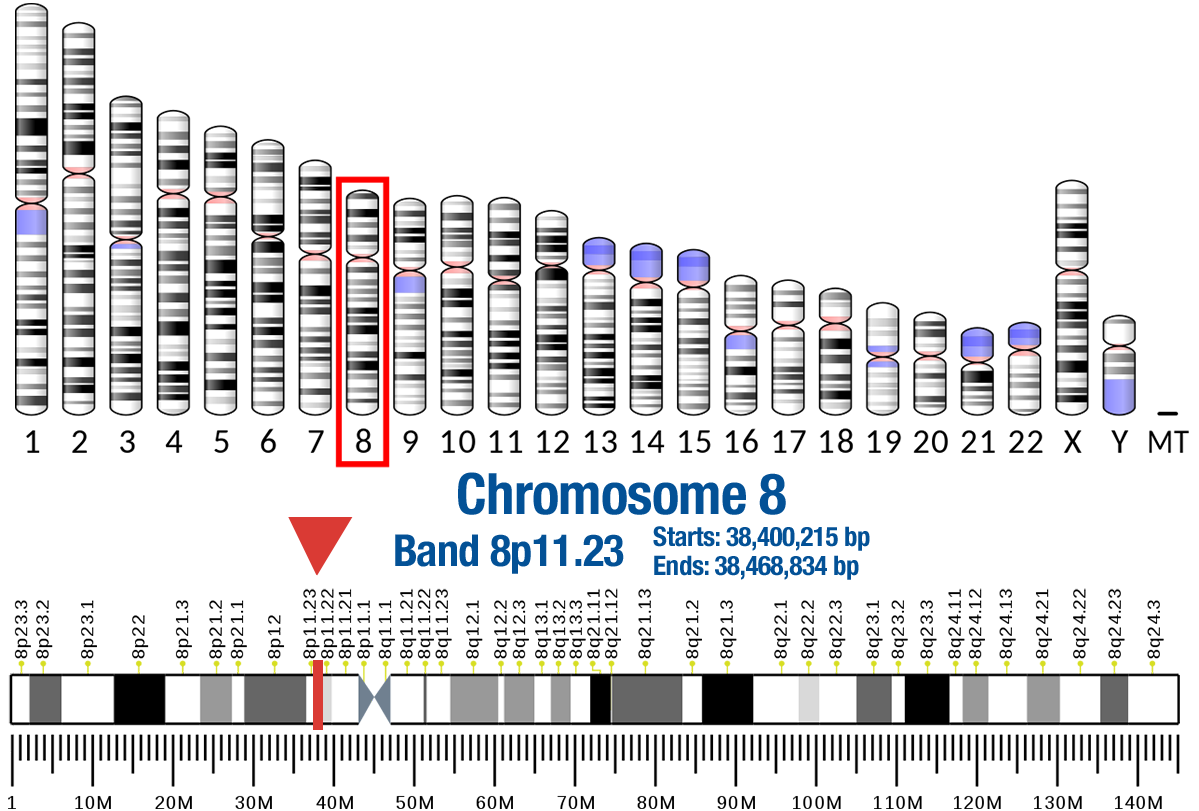
Gene Location