The protein encoded by this gene is a tyrosine kinase and cell surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors. The encoded protein is involved in the regulation of several pathways, including cell proliferation, cell differentiation, cell migration, lipid metabolism, bile acid biosynthesis, vitamin D metabolism, glucose uptake, and phosphate homeostasis. This protein consists of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin-like domains, a single hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment, and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]
- Nucleotide binding
- Protein kinase activity
- Protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity
- Protein tyrosine kinase activity
- Enables transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
- Located in extracellular region
- Cytoplasm
- Located in endosome
- Located in endoplasmic reticulum
- Located in Golgi apparatus
- Protein phosphorylation
- Involved in transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway
- Involved in multicellular organism development
- Acts upstream of or within positive regulation of cell population proliferation
- Acts upstream of or within fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays a role in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation and migration, and in regulation of lipid metabolism, bile acid biosynthesis, glucose uptake, vitamin D metabolism and phosphate homeostasis. Required for normal down-regulation of the expression of CYP7A1, the rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid synthesis, in response to FGF19. Phosphorylates PLCG1 and FRS2. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Promotes SRC-dependent phosphorylation of the matrix protease MMP14 and its lysosomal degradation. FGFR4 signaling is down-regulated by receptor internalization and degradation; MMP14 promotes internalization and degradation of FGFR4. Mutations that lead to constitutive kinase activation or impair normal FGFR4 inactivation lead to aberrant signaling.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Breast Cancer
- Gliomatosis Cerebri
- Sotos Syndrome
- Soft Tissue Sarcoma
- Parameningeal Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Neuroma
- Thanatophoric Dysplasia, Type I
- Outlet Dysfunction Constipation
- Orbit Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Craniosynostosis
- Achondroplasia, Severe, With Developmental Delay And Acanthosis Nigricans
- Constipation
- Functional Diarrhea
- Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Lacrimoauriculodentodigital Syndrome
- Crouzon Syndrome
- Hepatocellular Clear Cell Carcinoma
- Hypochondroplasia
- Colorectal Cancer
- Skeletal Muscle Cancer
- Hypophosphatemic Rickets, X-Linked Dominant
- Orbit Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Frontal Convexity Meningioma
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma
- Muscle Cancer
FGFR4 Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
The protein encoded by this gene is a tyrosine kinase and cell surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors. The encoded protein is involved in the regulation of several pathways, including cell proliferation, cell differentiation, cell migration, lipid metabolism, bile acid biosynthesis, vitamin D metabolism, glucose uptake, and phosphate homeostasis. This protein consists of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin-like domains, a single hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment, and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]
- Nucleotide binding
- Protein kinase activity
- Protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity
- Protein tyrosine kinase activity
- Enables transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
- Located in extracellular region
- Cytoplasm
- Located in endosome
- Located in endoplasmic reticulum
- Located in Golgi apparatus
- Protein phosphorylation
- Involved in transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway
- Involved in multicellular organism development
- Acts upstream of or within positive regulation of cell population proliferation
- Acts upstream of or within fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays a role in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation and migration, and in regulation of lipid metabolism, bile acid biosynthesis, glucose uptake, vitamin D metabolism and phosphate homeostasis. Required for normal down-regulation of the expression of CYP7A1, the rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid synthesis, in response to FGF19. Phosphorylates PLCG1 and FRS2. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Promotes SRC-dependent phosphorylation of the matrix protease MMP14 and its lysosomal degradation. FGFR4 signaling is down-regulated by receptor internalization and degradation; MMP14 promotes internalization and degradation of FGFR4. Mutations that lead to constitutive kinase activation or impair normal FGFR4 inactivation lead to aberrant signaling.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Breast Cancer
- Gliomatosis Cerebri
- Sotos Syndrome
- Soft Tissue Sarcoma
- Parameningeal Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Neuroma
- Thanatophoric Dysplasia, Type I
- Outlet Dysfunction Constipation
- Orbit Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Craniosynostosis
- Achondroplasia, Severe, With Developmental Delay And Acanthosis Nigricans
- Constipation
- Functional Diarrhea
- Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Lacrimoauriculodentodigital Syndrome
- Crouzon Syndrome
- Hepatocellular Clear Cell Carcinoma
- Hypochondroplasia
- Colorectal Cancer
- Skeletal Muscle Cancer
- Hypophosphatemic Rickets, X-Linked Dominant
- Orbit Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Frontal Convexity Meningioma
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma
- Muscle Cancer
FGFR4 Localizations – Subcellular Localization Database
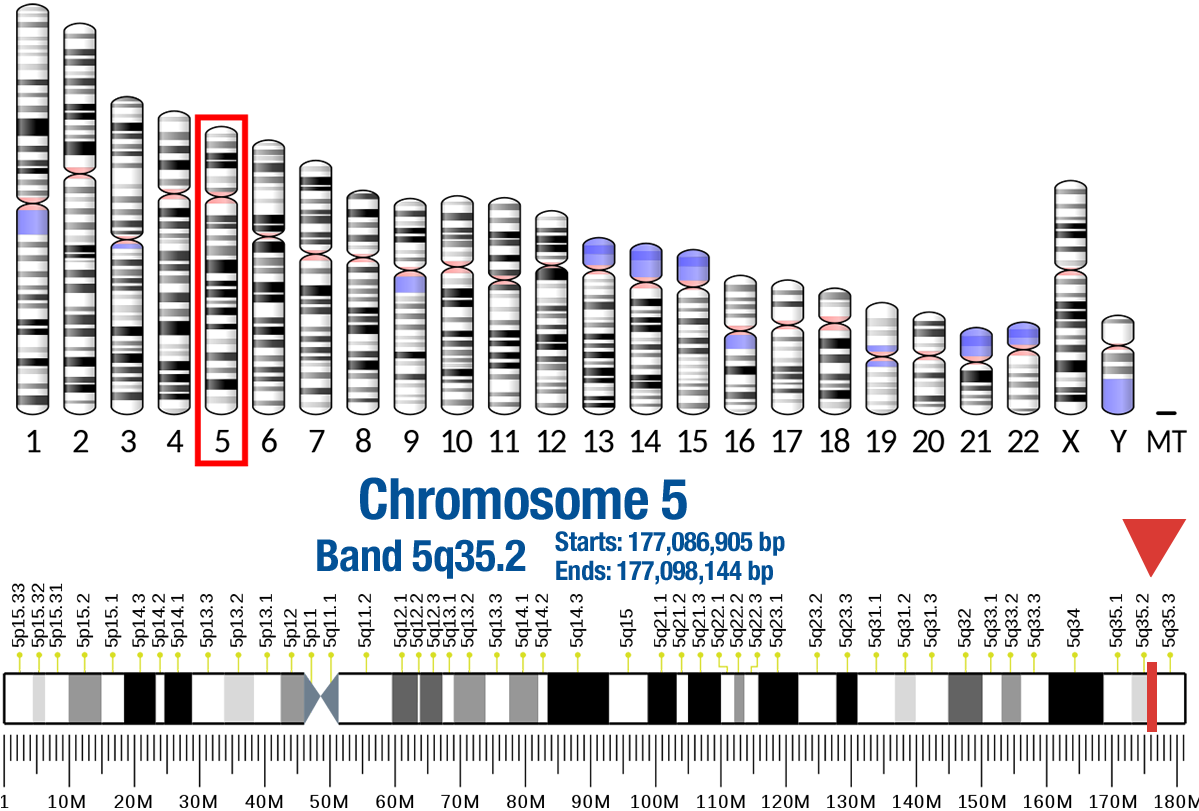
Gene Location