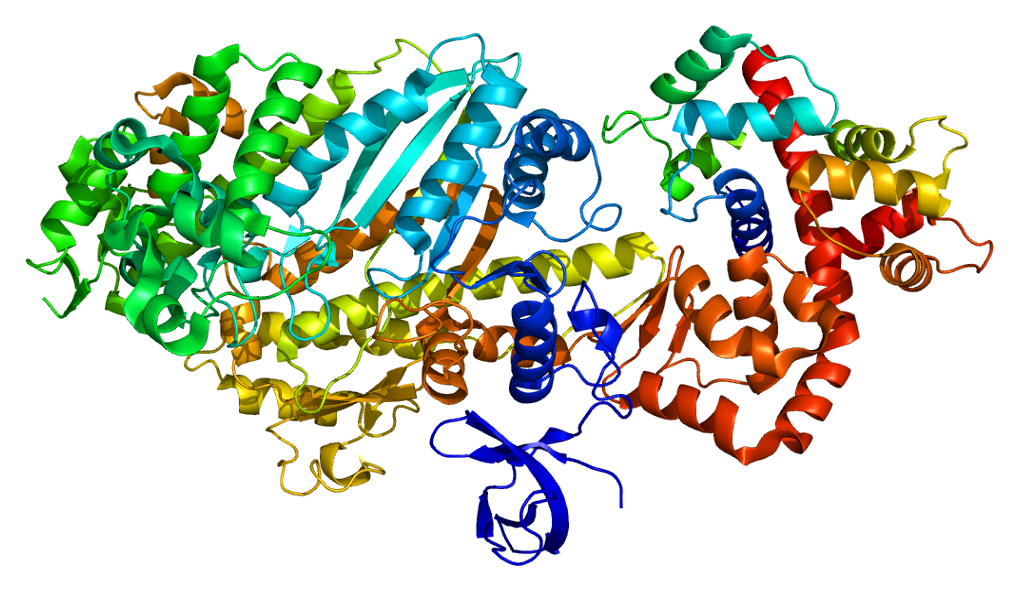
This gene encodes a reverse-direction motor protein that moves toward the minus end of actin filaments and plays a role in intracellular vesicle and organelle transport. The protein consists of a motor domain containing an ATP- and an actin-binding site and a globular tail which interacts with other proteins. This protein maintains the structural integrity of inner ear hair cells and mutations in this gene cause non-syndromic autosomal dominant and recessive hearing loss. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]
- Intracellular protein transport
- Endocytosis
- Actin filament organization
- Sensory perception of sound
- Protein transport
- Deafness, autosomal dominant 22
- Deafness, autosomal recessive 37
- Rare genetic deafness
- Autosomal dominant non-syndromic sensorineural deafness type dfna
- Autosomal recessive non-syndromic sensorineural deafness type dfnb
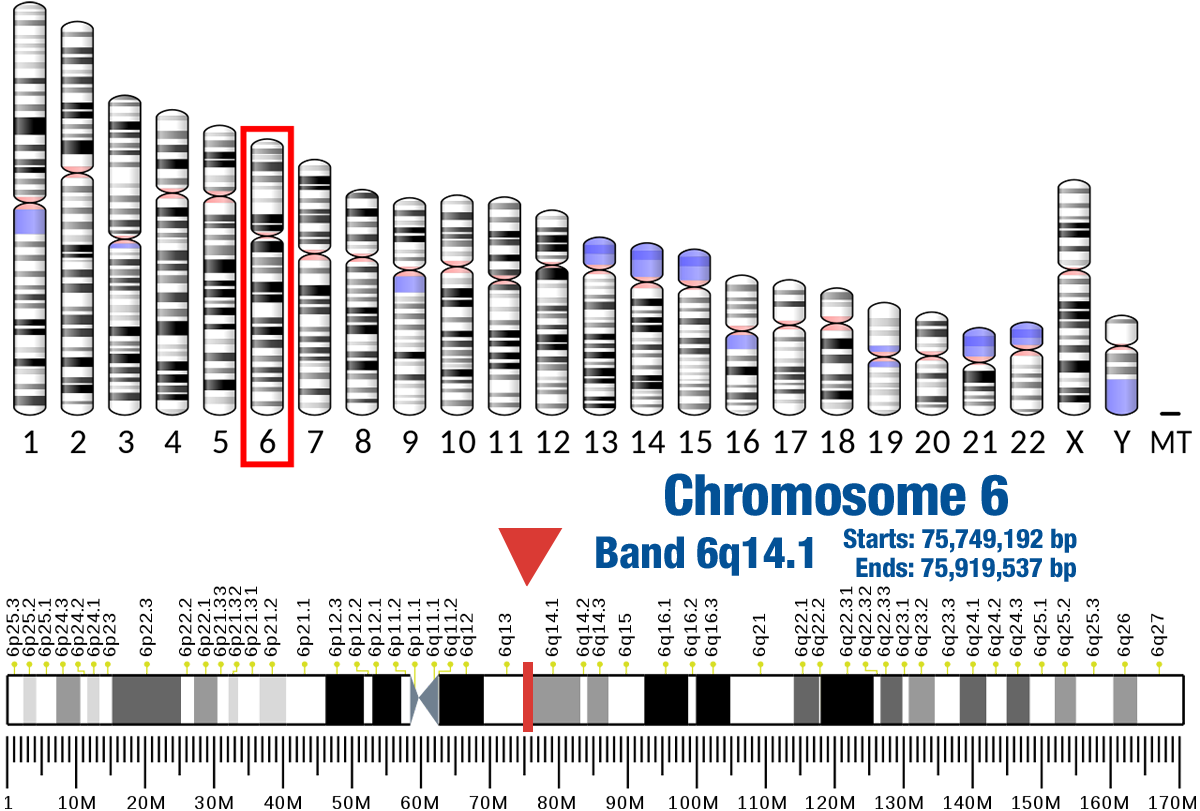
Gene Location