
Striated muscle in vertebrates comprises large proteins which must be organized properly to contract efficiently. Z-lines in striated muscle are a sign of this organization, representing the ends of actin thin filaments, titin, nebulin or nebulette and accessory proteins required for structure and function. This gene encodes a protein which interacts with nebulin in skeletal muscle or nebulette in cardiac muscle and alpha-actinin. In addition, this gene product can interact with a protein with the I-band indicating it has a regulatory as well as structural function. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]
- Homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules
- Axon guidance
- Sarcomere organization
- Dendrite self-avoidance
- Cardiomyopathy, dilated, 1kk
- Nemaline myopathy 11, autosomal recessive
- Cap myopathy
- Familial isolated restrictive cardiomyopathy
- Childhood-onset nemaline myopathy
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- General Cardiomyopathy
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Based on Ayass Bioscience, LLC Data Analysis
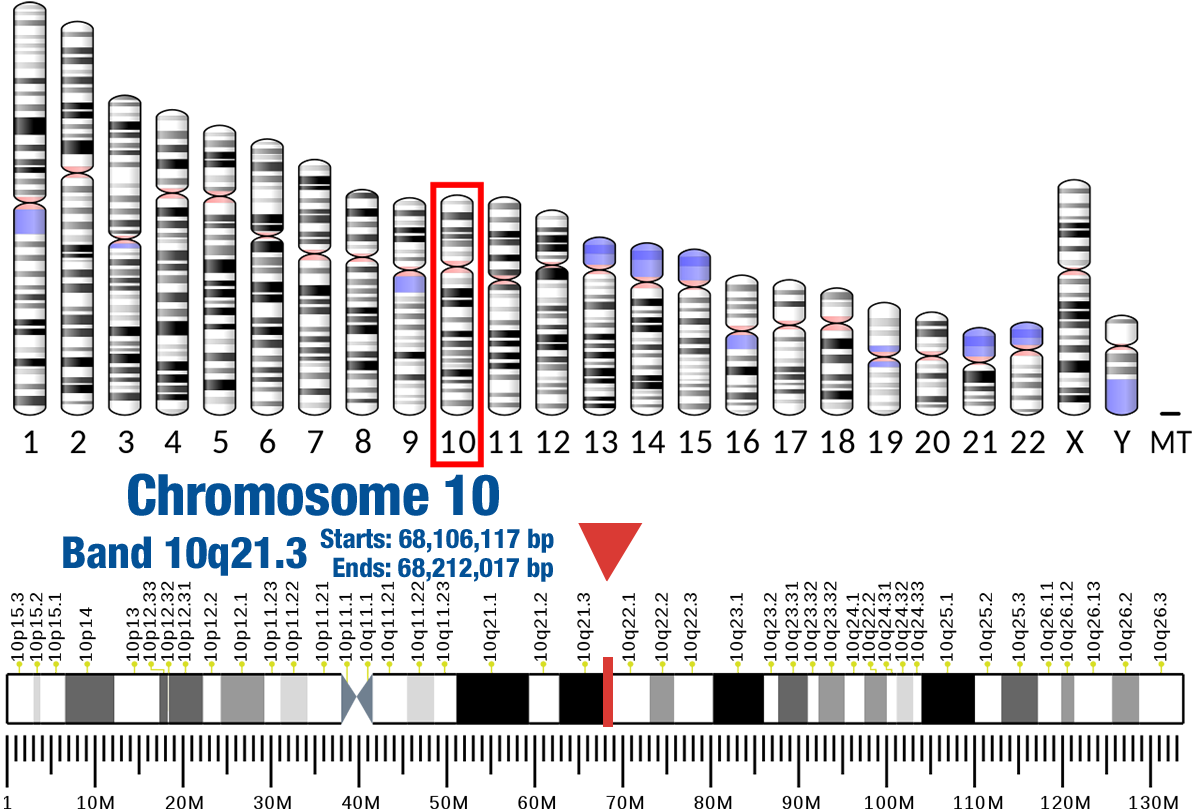
Gene Location
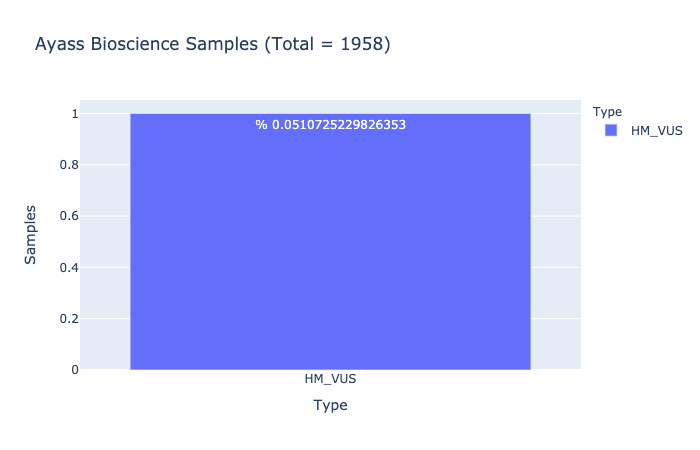
HM-VUS Prevalence
% 0.0510725229826353
Ratio of samples with at least 1 High/Med VUS variant (Computed from Ayass Bioscience Samples)
High/Med VUS Variants
A=0.000255(64/251060,GnomAD_exome)
A=0.000717(90/125568,TOPMED)
A=0.000256(31/120970,ExAC)
A=0.00002(2/85994,ALFAProject)
A=0.00111(87/78698,PAGE_STUDY)
A=0.00070(22/31356,GnomAD)
A=0.00031(4/13006,GO-ESP)
A=0.0006(3/5008,1000G)
A=0.0007(2/2922,KOREAN)
A=0.0005(1/1832,Korea1K)

