Voltage-gated sodium channels are heteromeric proteins that function in the generation and propagation of action potentials in muscle and neuronal cells. They are composed of one alpha and two beta subunits, where the alpha subunit provides channel activity and the beta-1 subunit modulates the kinetics of channel inactivation. This gene encodes a sodium channel beta-1 subunit. Mutations in this gene result in generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus, Brugada syndrome 5, and defects in cardiac conduction. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]
- Regulation of sodium ion transport
- Ion transport
- Sodium ion transport
- Cell adhesion
- Axon guidance
- Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus, type 1
- Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 52
- Atrial fibrillation, familial, 13
- Brugada syndrome 5
- Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus
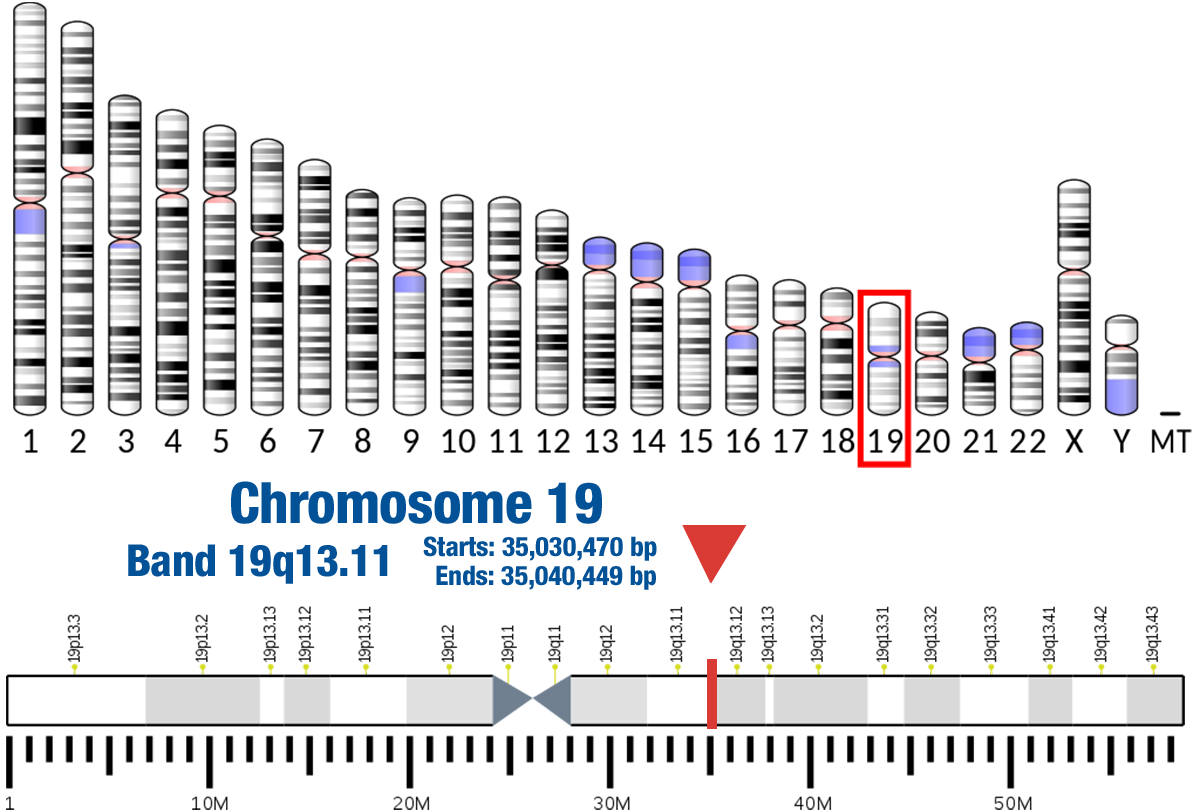
Gene Location